April 16, 2025
The 2024 ‘Honey Pot’ data breach in El Salvador was a wake-up call. Nearly 80% of the country’s population had their personal records, including facial images, exposed. As this incident resurfaces on social media, it raises critical questions about what truly makes biometric authentication secure.
But here’s what many commentators miss: this breach, while alarming for privacy reasons, doesn’t compromise biometric authentication systems with liveness detection capabilities. Understanding why means dispelling a common misconception.
In this article, we’ll explain the difference between privacy protection and authentication security in biometric systems, and distinguish between how biometric data is stored and how it’s used to verify identity.
A Common Misconception: The Myth of Facial Secrecy
Many people assume that biometric security depends on keeping your facial image secret, as if your face were a password that must remain hidden. The idea is that if your face remains hidden, so does your identity, and therefore the service you’re using stays secure.
In our digital age, the reality is that our face is already public. Think of:
- Professional photos on LinkedIn
- Personal images across social media
- Government-issued ID photos
- Security camera footage in public spaces
An attacker can easily find a photo on social media without having to breach a secure database. If biometric security hinges solely on the secrecy of a face, then posting your photo on Instagram would be a huge security risk.
An attacker doesn’t need to breach a secure database to find your face – they can simply visit your public profiles. Yet biometric authentication systems continue to secure billions of transactions daily. How?
Just because someone sees your face or an image of it doesn’t allow them to replicate the exact conditions required for authentication without your presence. The real challenge lies in verifying that the person trying to access a system is actually the right person, a real person, authenticating in real time – something a static image is unable to prove.
Privacy vs. Security: A Critical Distinction
Stored biometric information must be encrypted and safeguarded. but primarily to respect individual privacy rights and remain compliant, not because their exposure compromises biometric security.
Privacy and security, while related, serve different purposes in biometric systems:
- Privacy protection concerns how personal data is stored, accessed, and used. It’s about respecting individuals’ rights to control their information and preventing unauthorized access to that data.
- Authentication security focuses on one crucial question: Is the person attempting access genuinely who they claim to be, authenticating in real-time?
The El Salvador breach, while representing a serious privacy violation, doesn’t necessarily create a security vulnerability in properly designed authentication systems.
While encrypting biometric data is essential for privacy, the true measure of security is whether the system can confirm that the person accessing it is actually present at the moment of the transaction.
The Real Foundation of Biometric Security
What truly protects against impersonation attempts is a combination of underlying technologies and algorithms that determine the genuine human is present in real time – not a replay, deepfake, or digital injection attack.
When a science-based biometric authentication solution is implemented, stolen images become worthless in attacks. They cannot be used to trick a sophisticated biometric liveness detection system that determines whether the real person is authenticating at that moment.
Even if an attacker gains access to a database of facial images, those images would be useless if the system requires live proof of presence. A static photo or even a deepfake would fail the science-based liveness test.
Advanced biometric systems require proof that:
- A real human (not a photo or deepfake) is present
- This specific person (matching stored credentials) is authenticated
- The authentication is happening now (not replayed from a previous session)
Learn more about the privacy and security processes/accreditations of our system in the new Security & Architecture eBook.
Moving Beyond Template Security
Many organizations focus heavily on how to store biometric data securely – splitting and encrypting it across multiple locations, much like storing pieces of a valuable painting in different high-security vaults.
iProov’s technology uses a privacy firewall. iProov has no access to other information apart from the face, and the organization using iProov has no access to the biometric data. There is a structural separation between the user identity and the user biometric, which is highly effective in safeguarding the privacy of the user.
But the security of biometric authentication doesn’t depend on how well we store facial images or biometric templates – it depends on the system’s ability to detect and prevent impersonation attempts during the authentication event itself.
Science-Based Liveness Detection
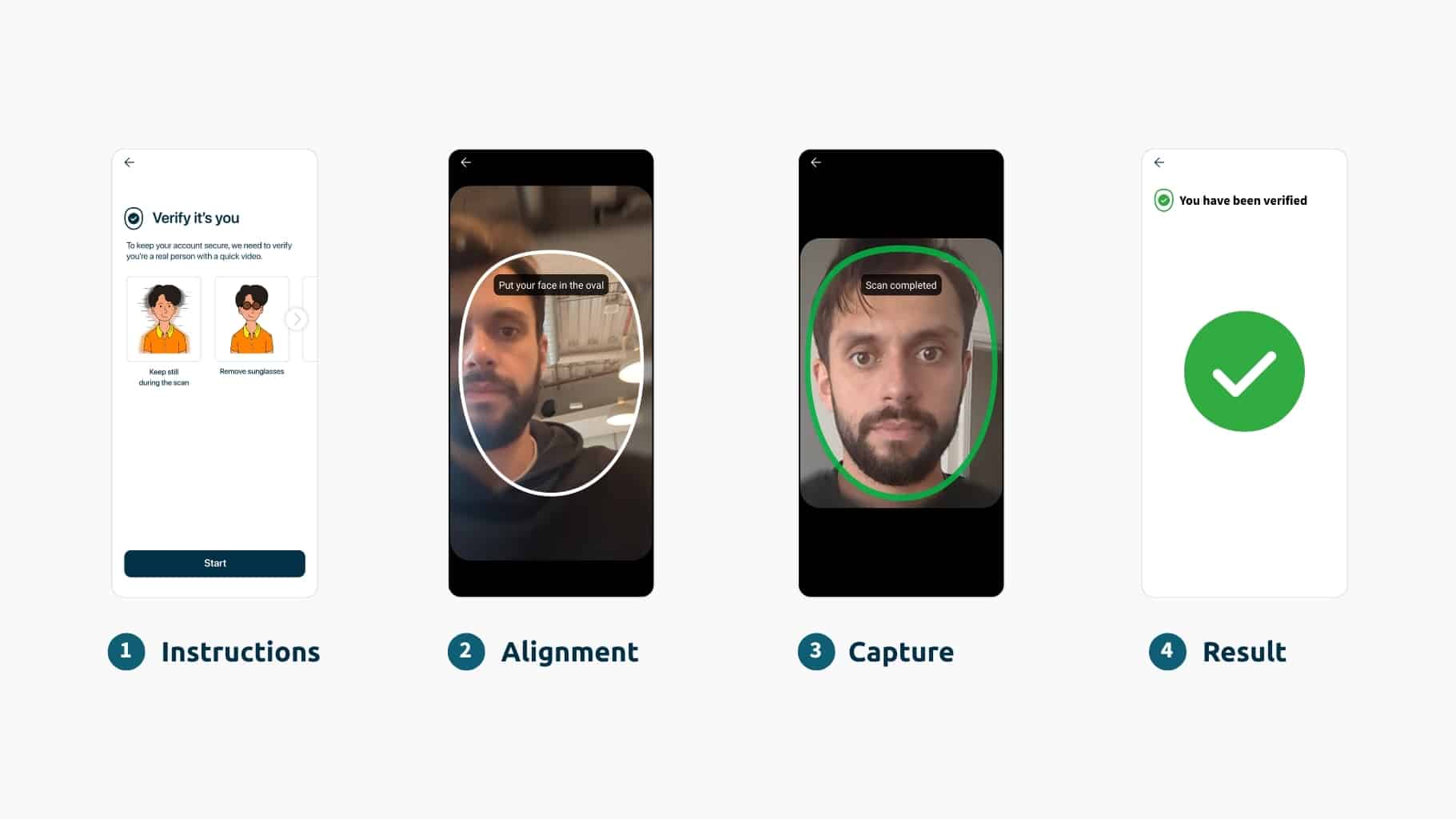
Establishing real-time authenticity is one of the most pressing challenges in biometric security. To accomplish this, passive challenge-response liveness detection technology is required; it forms the true foundation of secure biometric authentication. Unlike active challenge responses, like a head turn, a passive challenge response has no complex instructions and delivers high performance across demographics.
iProov Dynamic Liveness verifies it’s a real person and they’re authenticating in real time, delivering the highest level of identity assurance and mission-critical deepfake defense. The advanced security levels are achieved by patented Flashmark™ technology, which illuminates the device screen during the face capture process. The reflection of light on the individual’s face confirms they’re genuinely present and delivers advanced mitigation of zero-day AI-based attacks, including deepfakes and face swaps.
Looking Forward
The El Salvador breach highlights a crucial truth: in a world increasingly threatened by sophisticated deepfakes and digital injection attacks, the security of biometric systems will depend more than ever on their ability to verify genuine human presence. By focusing on science-based liveness with real-time verification, organizations can create a security environment where stolen data cannot be repurposed for impersonation.
The lesson from El Salvador isn’t that biometric authentication is flawed; it’s that faces are not the key to biometrics – liveness detection is. With proper liveness detection in place, biometric authentication remains one of our strongest tools against identity fraud.
As biometric authentication becomes increasingly central to our digital lives – from banking to healthcare to government services – choosing the right technology partner is crucial.
iProov takes privacy and security seriously – our technology is certified by FIDO and ISO, and is compliant with GDPR, SOC 2, and eIDAS (and others – learn more), providing the highest level of identity assurance to reduce fraud and protect your organization. Ready to see how our advanced authentication solutions can safeguard your users? Book your demo today.