June 11, 2023
In today’s digital era, the demand for robust identity verification and security measures has surged. Traditional methods like passwords, One-Time Passcodes (OTPs), and video call verification are failing organizations and users alike.
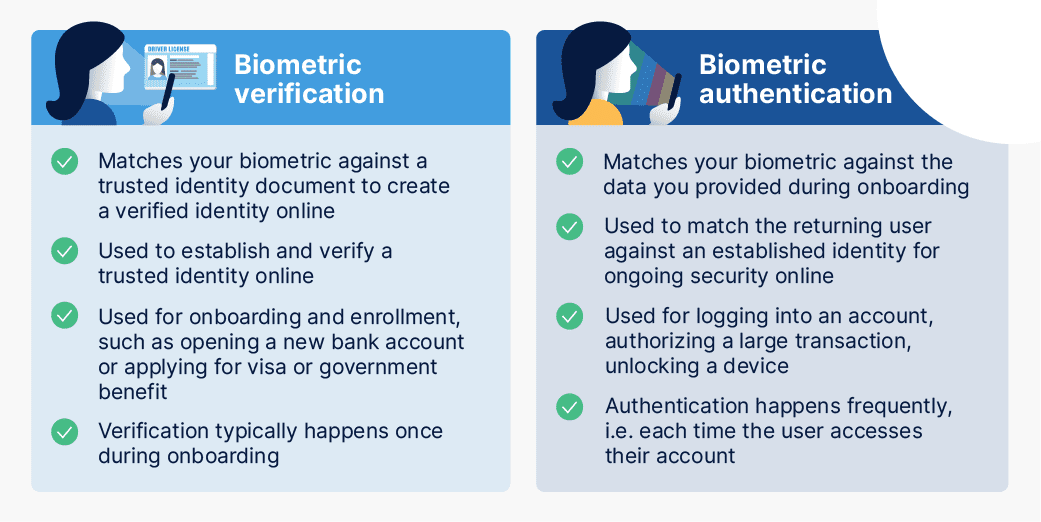
Biometric facial verification stands out as the most secure and user-friendly way of proving identity online, but there are many different companies to choose from.
To assist you, we’ve crafted a comprehensive guide to ensure you make an informed decision that aligns perfectly with your organization’s needs. Let’s walk through your top considerations when evaluating biometric vendors.
1. Evaluate Security
The very first step is to determine the levels of security required and identify risks in your own organization. What are the implications of account takeover? For banks, this could mean an account being emptied or large sums of money being stolen.
What damage could be caused to your organization by allowing criminals to set up fraudulent accounts using a stolen or synthetic identity? If you’re in the financial sector, fraudsters can set up accounts for money laundering, and you risk being prosecuted by the regulators for failing to follow know-your-customer (KYC) or anti-money laundering (AML) guidelines. If you’re a government agency, fraudsters could steal money allocated for social benefits.
The potential scale of the problem should also be considered, as a mass-scale attack could lead to thousands of successfully compromised accounts in a short period of time.
From there, you can assess the biometric vendor’s defenses. Here’s a list of areas you can ask the vendor about:
- Spoof detection:
- Inquire about the vendor’s anti-spoofing capabilities. How do they detect and prevent presentation attacks (e.g., photos, videos, or 3D masks)? Presentation attack detection (PAD) can detect attacks such as masks and paper printouts.
- Can the solution defend against more sophisticated attacks that the industry currently does not certify defense against – such as digitally injected attacks, deepfakes, and generative AI attacks?
- Determine how far the vendor’s deployments have been tested by externally accredited penetration testing agencies or a government’s own Red Team.
- Liveness detection:
- Does the solution incorporate liveness checks? How has their liveness technology been tested and accredited?
- What techniques are used? Single-frame liveness provides little protection for organizations, and mutli-frame liveness is recommended. Is the solution passive or active?
- Evolving security:
- How do the vendor’s defenses stay ahead of the evolving threat landscape? Ask: how do you defend against zero-day threats? What meta and imagery data are you analyzing as part of your threat detection methods? How do you protect the integrity of your software from cyber attacks such as emulators?
- A Security Operations Centre (SOC) is vital to detecting and preventing generative AI, deepfakes, face swaps, and metadata manipulation techniques on an ongoing basis.
2. Assess Usability And Inclusivity
Usability and inclusivity determine how the biometric solution will be accepted and embraced by users. Your biometric solution should be usable by the largest section of the population possible. Ensuring inclusivity is not only the right thing to do, but also expands your total addressable market and therefore can maximize revenue. Here are some areas to cover:
- Inclusivity: Can the vendor demonstrate how they actively mitigate against bias? Do they already support customers in multiple regions and for diverse customer populations? Do they train their algorithms on diverse data sets? Is the solution accessible by digital newbies as well as digital natives? Can it be used on any device – what types, makes, and models do they support
- Certification: Is the biometric vendor conformant to WCAG 2.2 AA and 508?
- Usability and convenience: Can users complete the authentication easily? What techniques are implemented to support completion rates and mitigate friction? Can it demonstrate improved performance and high success rates?
3. Address Privacy Concerns
When selecting a vendor, ask the following questions:
- How and where is the data being processed and stored? What types of security measures are in place to protect the biometric data collected?
- How is the vendor complying with regulations? Is the organization ISO 27001, SOC 2 Type II certified?
- How do you handle data retention, deletion, and compliance with data protection regulations, such as GDPR?
- What is the disaster recovery and business continuity plan in case of system failures or other emergencies?
- For EU organizations: is your organization compliant and audited to eIDAS Level of Assurance High?
4. Compare System Accuracy And Performance
If an authentication fails, for whatever reason, a user’s frustration will increase. This, in turn, affects your brand image and customer satisfaction as well as cost. Ask: what is the accuracy rate of your facial verification technology, and how do you measure it? What are your average attempts to pass and in-production completion rates? Evaluate the following areas:
- Number of attempts to pass: When evaluating a product’s performance, ask for the average number of attempts genuine users need to pass authentication. While the goal is for every legitimate user to pass on the first attempt, some failures are inevitable. The extent to which the average number of attempts exceeds one indicates the product’s usability and likely conversion rate. Request this metric from the vendor, along with the sample size and calculation method used. Additionally, gather feedback from existing customers to gain insights into their experiences.
- False Acceptance Rates (FAR) and False Rejection Rates (FRR): It’s important to establish the vendor’s FRR and FAR to measure this quantitatively. The quality of a vendor’s liveness technology will impact FAR and FRR.
- Device-based performance: How does the vendor ensure consistent performance (high completion rates) regardless of the device used?
5. Understand Your Scalability Needs
When implementing biometric authentication, many organizations are uncertain about the level of user adoption. Projected demand might differ significantly from actual outcomes. You need to ensure that the solution you choose will scale quickly and cost-effectively. If you host the solution yourself, can you provision and afford the servers needed to cover all outcomes? If you opt for a cloud-based provider, evaluate their track record in handling high levels of demand.
6. Compare Costs
The pricing of biometric systems can vary and may include different components. For example, some cloud vendors include hosting costs in their pricing, while others expect the organization to bear these expenses directly. To find the best option for your budget, create several potential usage models and work with the vendor to determine the most suitable model.
Ask: Can you provide information about the cost structure of your facial biometric verification service, including any licensing fees, subscription models, or additional costs?
7. Understand The Vendor’s Level of Human Intervention
Explore how vendors manage human intervention in their processes. Manual intervention has implications for both privacy and accuracy. Manual checks also lack scalability; vendors may struggle to double their workforce if the workload unexpectedly doubles. Additionally, human-operated systems struggle to consistently and accurately identify synthetic media like deepfakes.
Human, hybrid, and automated biometric verification processes can be split into five categories:
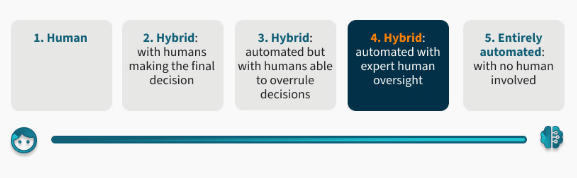
To reap the benefits of biometric technology, it is advisable to deploy hybrid, automated identity verification processes that leverage human experts for real-time supervision. This approach ensures reliable, consistent results
It must be noted that all remote identity verification methods are vulnerable to synthetic media attacks (such as deepfakes), whether that be human-operated video verification calls, hybrid processes with facial biometric checks and human oversight, or fully automated processes. Read more about the threats to remote identity verification systems here.
8. Evaluate Level of Assurance
Consider:
- The Level of Assurance (LoA): LoA refers to the certainty you can have that an identity can be trusted to actually be the claimant’s “true” identity. The higher the assurance level, the more secure the identity and the lower the risk of successful attacks such as new account fraud, synthetic identity fraud, and identity takeover. Ask: How does the technology determine real-time authentication, ensuring that is not a replay of a previous authentication? Do they offer different levels of assurance to accommodate different use cases and risk appetite (e.g., low-security access vs. high-security transactions)?
- The customer’s perception of assurance: To strike the right balance between speed and security, think carefully about the scenarios you’ll be serving. A split-second authentication may not offer the reassurance needed if a user is completing a high-value transaction, but an authentication that takes 30 seconds may cause frustration.
9. Consider The Vendor’s Deployment And Integration
Ask: How is the technology deployed? And, on average, how long does it take to deploy in production? What kind of hardware or software is required to integrate the facial verification solution into your existing infrastructure?
Can your system handle a large number of simultaneous requests in real-time? What is the processing speed and transactions per second (TPS) that it can handle? Will I get a dedicated point of contact? What steps will they take to improve our business outcomes? How can I measure performance? Do you have 24/7, real-time reporting capabilities?
10. Check The Vendor’s Profile And References
- Does the vendor have a strong presence in the industry? Are they involved in setting standards and working with other organizations to define the future of the industry? Has the vendor won any awards? Choose a vendor that is reputable, is proven, has good references, and can demonstrate strong market adoption.
- Who are they working with and what testing and audits have they been through? For instance, choosing a vendor with a global customer base might be crucial in providing reassurance on bias and inclusivity.
- Are they easy to work with? Do they have customer-focused people and processes? What do their other customers and partners say about them?
If you’d like to learn more about how iProov can secure and streamline your organization’s online verification, authentication, and onboarding, book your demo today.